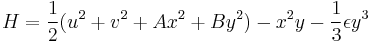Hénon-Heiles equation
The Henon-Heiles equation is used to model stars. It is expressed as
While at Princeton in 1964, Michel Hénon and Carl Heiles published a paper that describes the non-linear motion of a star around a galactic center where the motion is restricted to a plane.
The Henon-Heiles System (HHS) is defined by the following four equations:
where 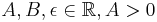 and
and  . Since HHS is specified in
. Since HHS is specified in 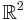 , we need a Hamiltonian of degrees of freedom two to model it.
, we need a Hamiltonian of degrees of freedom two to model it.
It can be solved for some cases using Painleve Analysis. The Hamiltonian for the HHS is